Köppen-Geiger-Photovoltaic climate classification
The Köppen-Geiger-Photovoltaic climate classification (KGPV) is a way of classifying different climates based on parameters relevant for photovoltaic systems [1]. It divides Earth into 12 zones with regard to temperature, precipitation, and irradiation. The zones are composed of two classification levels: 5 Temperature-Precipitation (TP-) zones and 4 Irradiation (I-) zones.
Zone definition
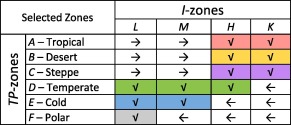
Temperature-Precipitation (TP-) zones are defined as:
- A – Tropical
- B – Desert
- C – Steppe
- D – Temperate
- E – Cold
- F – Polar
Irradiation (I-) zones are defined as:
- L – Low
- M – Medium
- H – High
- K – Very High
The limits between the I-zones correspond to the 30th, 50th, and 80th irradiation percentiles: 1130, 1560, and 2070 kWh/m², respectively.
The combination of these 2 levels should lead to 24 climate zones. However, the model was further simplified by merging zones with low population density and/or low land surface area to keep only 12 zones. The zone-merging process is described in the table below (from [1]).
KGPV map
The 12 KGPV zones retained are shown on the map below.
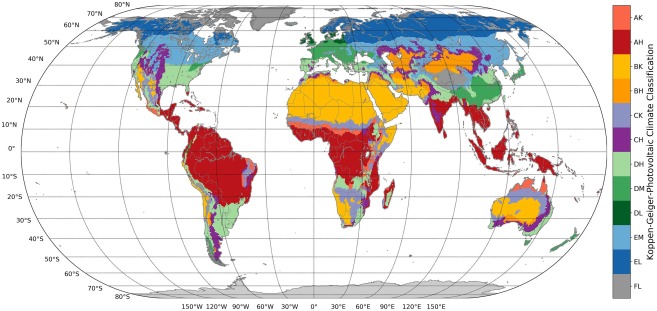
Fig. Köppen-Geiger-Photovoltaic climate classification with the 12 most relevant climate zones (Antarctica excluded), taken from [1].
[1] J. Ascencio-Vásquez, K. Brecl, and M. Topič, “Methodology of Köppen-Geiger-Photovoltaic climate classification and implications to worldwide mapping of PV system performance,” Sol. Energy, vol. 191, no. May, pp. 672–685, 2019, doi: 10.1016/j.solener.2019.08.072.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0038092X19308527